The Challenge
All large pharmaceutical companies assume high risk in attempts to bring drugs to market. Currently more and more can be outsourced to reduce failure risk before expensive clinical trial.
Modernize your drug development with GMLs
Modernize your drug development approach by taking advantage of cutting edge functional genomics with Gene Mutation/Function Libraries (GMLs). Through a massively parallel mammalian cell in vivo process called the GigaAssay, Heligenics produces what is called a Gene Mutation/Function Library (“GMLs”). Each GML measures the impact of all possible amino acid substitutions in the target upon its molecular function in live human cells.
GMLs have several applications in the drug development pipeline: screening lead compounds, evaluating derivatives, characterizing compounds ready for trials, and optimizing trial design for approval. Eliminate safety concerns and low efficacy before a trial. These are the major factors that produce much higher risk for the drug development and approval process.
Application of GMLs
GMLs have several applications in the drug development pipeline: screening lead compounds, evaluating derivatives, characterizing compounds ready for trials, and optimizing trial design for approval. Eliminate safety concerns and low efficacy before a trial. These are the major factors that produce much higher risk for the drug development and approval process.
Use GMLs at key process steps prior to an expensive trial:
- Identify amino acid positions and genetic variants of concern for safety – dose response/toxicity
- GMLs -/+ drug comparison to identify resistance variants in the population in advance.
- Identify minimum effective doses stratified by common genetic variants – time course/dose response
- Guide drug derivitization with GMLs by identifying amino acid substitutions that impact function near the drug binding site.
- Design clinical trials with stratification of trial arms or exclusion criteria based on important genetic variants frequent in the human population
To improve efficacy and safety, comparison of GMLs identifies all resistance substitutions, those in the drug binding site, and those causing cell toxicity, which are then compared to population allele frequencies. Those major alleles that produce resistance or toxicity defined by the GMLs guide candidate selection, drug derivitization, and trial design. In addition exclusion criteria or arm stratification could be provided for a clinical trial.
Example GML for a hypothetical gene
Shown below is a GML result for a fictitious gene; this table shows 5 variants from a table of over 10,000 SNVs (1). This type of GML has >97% of single nucleotide variants encoding single amino acid substitutions. For the Activity Metric (2), activity is measured against wild-type activity in the first column. A measurement of 100 is 1% of the wild-type (‘baseline’) activity. Pathogenicity (3) is determined from an activity threshold relative to wild-type activity and known pathogenic mutations.
Example results from a Gene Mutation / Function Library (GML) for a hypothetical gene is shown in the table below.
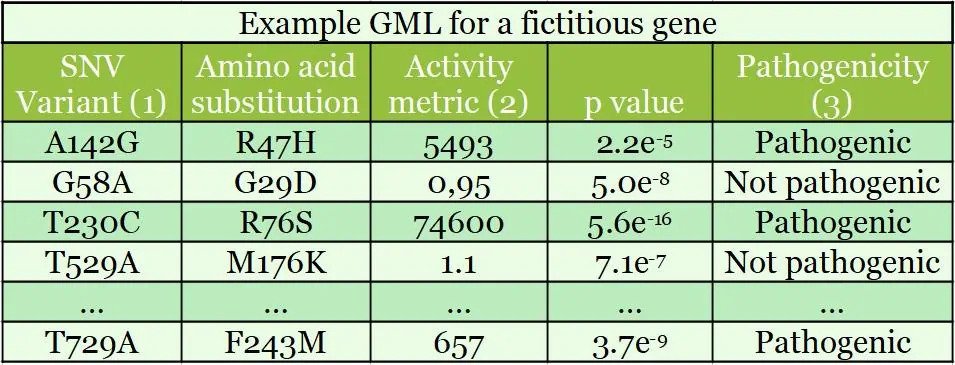
SNV = Single Nucleotide Variant; table shows 5 variants from a table of >30,000. Activity Metric value 100 = 1% of wildtype activity. Pathogenicity of known pathogenic mutations determines a threshold activity relative to wildtype.
Heligenics Drug Discovery Product Sheet Download
Kindly fill out the form below to access a handy PDF.
